Introduction
In recent years, a growing number of food and beverage brands have been rethinking their approach to sweeteners. Among the many alternatives to traditional cane sugar, beet root sugar has steadily emerged as a preferred choice for companies looking to align with consumer demand, sustainability goals, and evolving health trends. While cane sugar has long dominated the sweetener industry, beet root sugar is proving to be more than just a substitute – it’s becoming a strategic advantage.
Definition
Beet root sugar is a type of natural sweetener extracted from the roots of the sugar beet plant. It consists mainly of sucrose and is used as a substitute for cane sugar in cooking, baking, and food production. This sugar is valued for its similar sweetness and functionality to regular sugar while being derived from a plant-based source.
What is Beet Root Sugar?
Beet root sugar, often simply called “beet sugar,” is derived from the sugar beet plant, a root vegetable rich in sucrose. Unlike sugar cane, which grows in warm, tropical climates, sugar beets thrive in temperate regions, particularly across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. The extraction process involves washing, slicing, and boiling the beets, followed by crystallization to produce pure white sugar.
Chemically, beet sugar and cane sugar are nearly identical, consisting of sucrose molecules that taste the same to the human palate. However, differences in production, sustainability, cost, and supply chain logistics are making beet sugar the more attractive option for many food brands.
Rising Consumer Awareness Around Sugar Sources
Today’s consumers are more conscious about what goes into their food than ever before. With increasing transparency in food labeling and digital access to supply chain information, shoppers want to know not only how much sugar is in their favorite products, but also where that sugar comes from.
Food brands have recognized that sourcing matters. Beet sugar often appeals to consumers because it can be labeled as locally grown in many Western countries. Instead of importing cane sugar from overseas, companies can highlight domestic agriculture, which resonates with shoppers who prioritize local sourcing, reduced carbon footprints, and supply chain integrity.
Sustainability Advantages of Beet Root Sugar
Sustainability is one of the biggest reasons behind the shift. Producing beet root sugar has several environmental benefits compared to cane sugar:
Lower Water Usage:
Sugar cane is a water-intensive crop, often grown in regions already struggling with water scarcity. By contrast, sugar beets generally require less water and are grown in climates where rainfall often supplements irrigation.
Reduced Land Pressure:
Sugar cane requires large tracts of land and thrives only in tropical climates, often contributing to deforestation. Sugar beets, on the other hand, are rotational crops that fit into existing farmland, improving soil health and reducing monoculture practices.
Smaller Carbon Footprint:
Because sugar beets can be grown closer to manufacturing facilities in many Western countries, transportation emissions are significantly reduced. This local advantage is increasingly important for brands aiming to meet climate commitments.
Renewable Byproducts:
The byproducts of beet sugar processing – such as beet pulp and molasses – are often repurposed for livestock feed, biofuels, and fermentation industries, making the production process more circular and resource-efficient.
Cost Efficiency and Supply Chain Stability
Global supply chains are under more scrutiny and pressure than ever before. Sugar cane production is highly concentrated in a few regions such as Brazil, India, and Thailand. Political instability, climate change, and logistical challenges in these regions can create volatility in supply and pricing.
Beet sugar, on the other hand, offers diversification. For brands based in Europe or North America, sourcing from local beet farms reduces dependency on volatile global supply chains. It ensures a steady supply, predictable costs, and less risk of price spikes caused by shipping disruptions or import restrictions.
Moreover, modern agricultural techniques and genetic improvements have made sugar beet yields increasingly competitive with sugar cane, making beet sugar not just an environmentally conscious choice, but also an economically sound one.
Meeting Clean Label and Health Trends
Another factor driving the switch is the clean label movement. Consumers are pushing for foods with shorter, simpler ingredient lists and recognizable sources. Beet sugar aligns perfectly with this trend. Brands can market it as a natural sweetener derived from beets—an everyday vegetable rather than a tropical crop shrouded in industrial processing.
Additionally, beet sugar often carries fewer negative associations than cane sugar. While both are forms of sucrose and should be consumed in moderation, beet sugar benefits from its positioning as a “better” or more transparent option. This perception, even more than chemical differences, makes beet sugar attractive to brands aiming to appeal to health-conscious buyers.
The Organic and Non-GMO Factor
Organic and non-GMO certifications are highly sought after in the food industry, and beet sugar provides a strong foothold in this space. Many sugar beet crops, especially in Europe, are non-GMO by default due to strict agricultural regulations. This makes it easier for brands to achieve clean certifications without the added complexity of sourcing from regions where genetically modified cane varieties dominate.
Organic beet sugar production is also growing, and while more expensive, it offers food brands a premium ingredient to highlight in specialty or health-focused product lines.
Adoption Across the Food Industry
The shift to beet sugar is happening across multiple categories:
Bakeries and Confectionery: Beet sugar is being widely adopted in baked goods, candies, and chocolates, where its nearly identical taste to cane sugar ensures no loss in product quality.
Beverages: Soft drinks, juices, and flavored waters are beginning to feature beet sugar, especially in markets where local sourcing is a selling point.
Dairy and Plant-Based Products: Yogurts, ice creams, and alternative dairy brands are leaning into beet sugar as part of their clean label appeal.
Packaged Foods: From breakfast cereals to snack bars, beet sugar is becoming a staple ingredient that brands can highlight on packaging to attract label-conscious buyers.
This widespread adoption demonstrates that the trend is more than a niche—it’s reshaping the sugar market itself.
Challenges to Consider
Despite its advantages, the transition to beet sugar isn’t without challenges:
Consumer Education: Not all shoppers understand the difference between cane and beet sugar. Brands must invest in marketing and storytelling to communicate the benefits clearly.
Taste Perceptions: While beet and cane sugar are chemically identical, some chefs and manufacturers claim subtle differences in flavor, particularly in specialty applications like fine chocolate or caramelization.
Scaling Organic Production: Demand for organic beet sugar often outpaces supply, which can drive up costs and limit availability.
Still, these hurdles are relatively minor compared to the long-term gains in sustainability, cost stability, and consumer trust.
Future Trends of Beet Root Sugar Market
1. Growing Demand for Sustainable Sweeteners:
With increasing pressure on food companies to reduce their carbon footprint, beet root sugar is expected to gain traction as a more sustainable alternative to cane sugar, especially in regions focused on local sourcing.
2. Expansion of Organic and Non-GMO Beet Sugar:
The rising popularity of organic and clean-label products will drive demand for certified organic and non-GMO beet sugar, particularly in premium food and beverage categories.
3. Technological Advancements in Processing:
Innovations in extraction and refining will improve yield, quality, and cost efficiency, making beet sugar more competitive against cane sugar on a global scale.
4. Diversification Across Food and Beverage Segments:
From bakery and confectionery to plant-based and functional foods, beet sugar will increasingly be adopted across diverse product lines, expanding its market presence.
5. Market Expansion Beyond Europe and North America:
While Europe currently dominates beet sugar production, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show growing interest due to changing dietary preferences and sustainability goals.
Growth Rate of Beet Root Sugar Market
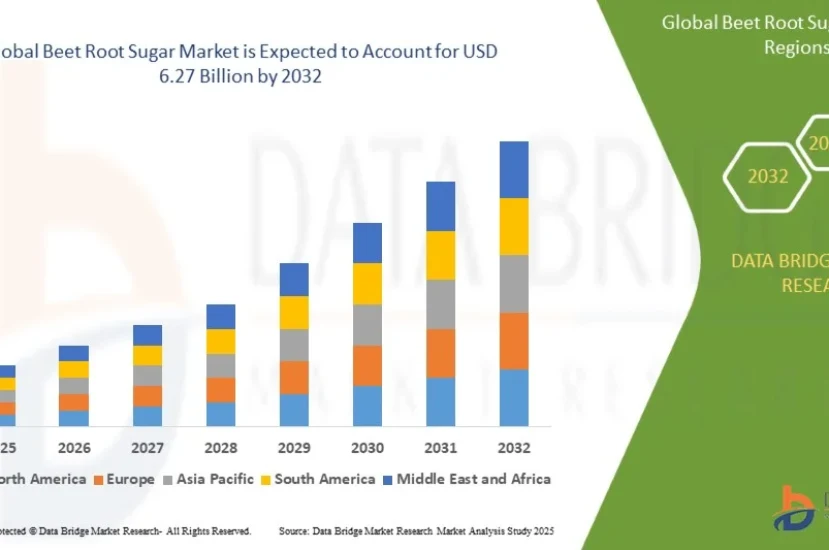
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the beet root sugar market was estimated to be worth USD 3.97 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% to reach USD 6.27 billion by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-beet-root-sugar-market
Conclusion
The transition from cane sugar to beet root sugar is emblematic of a larger movement in the food industry – toward sustainability, transparency, and consumer-centric innovation. For brands, beet sugar offers an appealing combination of local sourcing, environmental benefits, cost efficiency, and marketing potential. For consumers, it represents a sweetener that feels more in line with modern values and expectations.
Why Food Brands Are Switching to Beet Root Sugar



Leave a comment